As environmental concerns grow and more individuals seek healthier lifestyles, plant-based diets have risen in popularity. With the increasing emphasis on sustainability and the benefits of a plant-rich diet, people are turning towards plant-based eating for numerous reasons. Not only is this shift good for personal health, but it also has a positive impact on the environment.
Plant-based diets primarily focus on consuming foods derived from plants, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, while minimizing or eliminating meat and animal products. Research indicates that these diets can provide essential nutrients and promote overall health, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Moreover, plant-based diets have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to animal-based diets. The production of meat and dairy products is responsible for a substantial amount of greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. By adopting a plant-based diet, individuals can contribute to the reduction of these environmental impacts.
As more people recognize the benefits of plant-based diets for personal well-being and the planet, this dietary choice will likely continue to gain popularity.

Contents
- 1 Health benefits of a plant-based diet
- 2 Environmental benefits of a plant-based diet
- 3 Common misconceptions about plant-based diets
- 4 Getting started with a plant-based diet
- 5 Essential nutrients for a plant-based diet
- 6 Plant-based meal planning and recipes
- 7 Impact on weight loss
- 8 Plant-based diet and disease prevention
- 9 The future of plant-based food
- 10 Author
Health benefits of a plant-based diet
A plant-based diet offers numerous health benefits that contribute to overall well-being. By consuming a variety of plant-based foods, individuals can obtain essential nutrients and promote optimal health.
Firstly, plant-based diets are rich in fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight. Fiber also helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Foods such as legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources of fiber.
Additionally, plant-based diets are typically low in saturated fats and cholesterol, which can lower the risk of heart disease and stroke. Animal products, on the other hand, tend to be high in saturated fats and can contribute to cardiovascular problems. By replacing animal proteins with plant-based alternatives, individuals can improve their heart health.
Furthermore, plant-based diets are abundant in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients are essential for maintaining a strong immune system and preventing chronic diseases. Fruits and vegetables, in particular, are packed with vitamins A, C, and E, as well as various antioxidants that help protect the body against oxidative stress.
Environmental benefits of a plant-based diet
In addition to the health benefits, plant-based diets have a significant positive impact on the environment. The production of animal products, particularly meat and dairy, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution.
Animal agriculture is responsible for a substantial portion of global greenhouse gas emissions. The methane released by livestock has a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide. By reducing the demand for animal products, individuals can help mitigate climate change and reduce their carbon footprint.
Animal farming also requires large amounts of land and water resources. Deforestation is often necessary to create grazing land for livestock, which leads to the destruction of valuable ecosystems and habitats. Additionally, animal agriculture contributes to water pollution through the discharge of animal waste and the use of chemical fertilizers. By choosing plant-based alternatives, individuals can help conserve land and water resources.
Furthermore, plant-based diets can help address global food security. It takes significantly fewer resources to produce plant-based foods compared to animal products. By shifting towards a plant-based diet, we can effectively feed more people with the limited resources available.
Common misconceptions about plant-based diets
Despite the growing popularity of plant-based diets, there are still several misconceptions surrounding this dietary choice. Addressing these misconceptions can help individuals make informed decisions about adopting a plant-based lifestyle.
One common misconception is that plant-based diets lack sufficient protein. However, plant-based sources such as legumes, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, and hemp seeds are excellent sources of protein. By consuming a variety of plant-based protein sources, individuals can easily meet their protein needs.
Another misconception is that plant-based diets are expensive. While some plant-based products may have a higher price tag, a plant-based diet can be affordable. Staples such as grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables are often more budget-friendly than meat and dairy products. Additionally, cooking meals from scratch and buying seasonal produce can help reduce costs.
It is also often believed that plant-based diets are nutritionally inadequate. However, with proper planning and a varied diet, individuals can obtain all the necessary nutrients from plant-based sources. It is important to ensure an adequate intake of essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, which may require supplementation or careful food choices.
Getting started with a plant-based diet
Transitioning to a plant-based diet may seem challenging at first, but with the right approach, it can be a smooth and enjoyable process. Here are some tips for getting started:
- Gradual transition: Start by incorporating more plant-based meals into your diet and gradually reducing the consumption of animal products. This approach allows for a more sustainable and long-term change.
- Experiment with new recipes: Explore plant-based recipes and experiment with different ingredients and flavors. There are numerous resources available, including cookbooks, websites, and cooking classes, to help you discover delicious plant-based meals.
- Focus on whole foods: Emphasize whole, unprocessed plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods provide a wide range of nutrients and offer various culinary possibilities.
- Find plant-based alternatives: Discover plant-based alternatives to your favorite animal-based products. Nowadays, there are numerous plant-based meat substitutes, dairy-free milks, and vegan cheeses available in grocery stores and restaurants.
- Seek support: Join online communities or local plant-based groups to connect with like-minded individuals who can offer support, advice, and recipe ideas. Sharing experiences and challenges can make the transition easier.
Essential nutrients for a plant-based diet
While plant-based diets can provide all the necessary nutrients, it is important to pay attention to certain key nutrients to ensure optimal health.
One essential nutrient often associated with plant-based diets is vitamin B12. This vitamin is primarily found in animal-based products, and vegans may need to supplement or consume fortified foods to meet their B12 requirements. Fortified plant-based milks, cereals, and nutritional yeast are good sources of vitamin B12.
Iron is another nutrient to consider, as plant-based iron (non-heme iron) is not as readily absorbed by the body as heme iron found in animal products. However, consuming iron-rich plant foods such as lentils, spinach, tofu, and fortified cereals, along with foods high in vitamin C, can enhance iron absorption.
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health and heart health. While fish is a common source of omega-3s, plant-based sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts can provide the necessary omega-3 fatty acids. Alternatively, algae-based omega-3 supplements are available for those who prefer a supplement.
Calcium is often associated with dairy products, but plant-based sources such as fortified plant-based milks, tofu, tempeh, leafy greens, and sesame seeds are excellent alternatives for obtaining calcium. It is important to ensure an adequate intake of calcium, especially for those who avoid dairy products.
Plant-based meal planning and recipes
Meal planning is an essential aspect of maintaining a balanced plant-based diet. Here are some tips for effective meal planning:
- Include a variety of plant-based foods in your meals to ensure a wide range of nutrients.
- Prioritize whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables as the foundation of your meals.
- Experiment with different cooking methods and flavors to keep meals interesting and enjoyable.
- Plan meals in advance and consider batch cooking to save time and ensure you have nutritious meals readily available.
- Incorporate plant-based protein sources such as tofu, tempeh, beans, lentils, and quinoa in your meals to meet your protein needs.
Here are a few simple and delicious plant-based recipes to get you started:
- Chickpea and vegetable stir-fry with brown rice
- Lentil and vegetable curry with quinoa
- Roasted vegetable and hummus wrap
- Spinach and mushroom tofu scramble
- Quinoa salad with mixed greens, avocado, and roasted vegetables
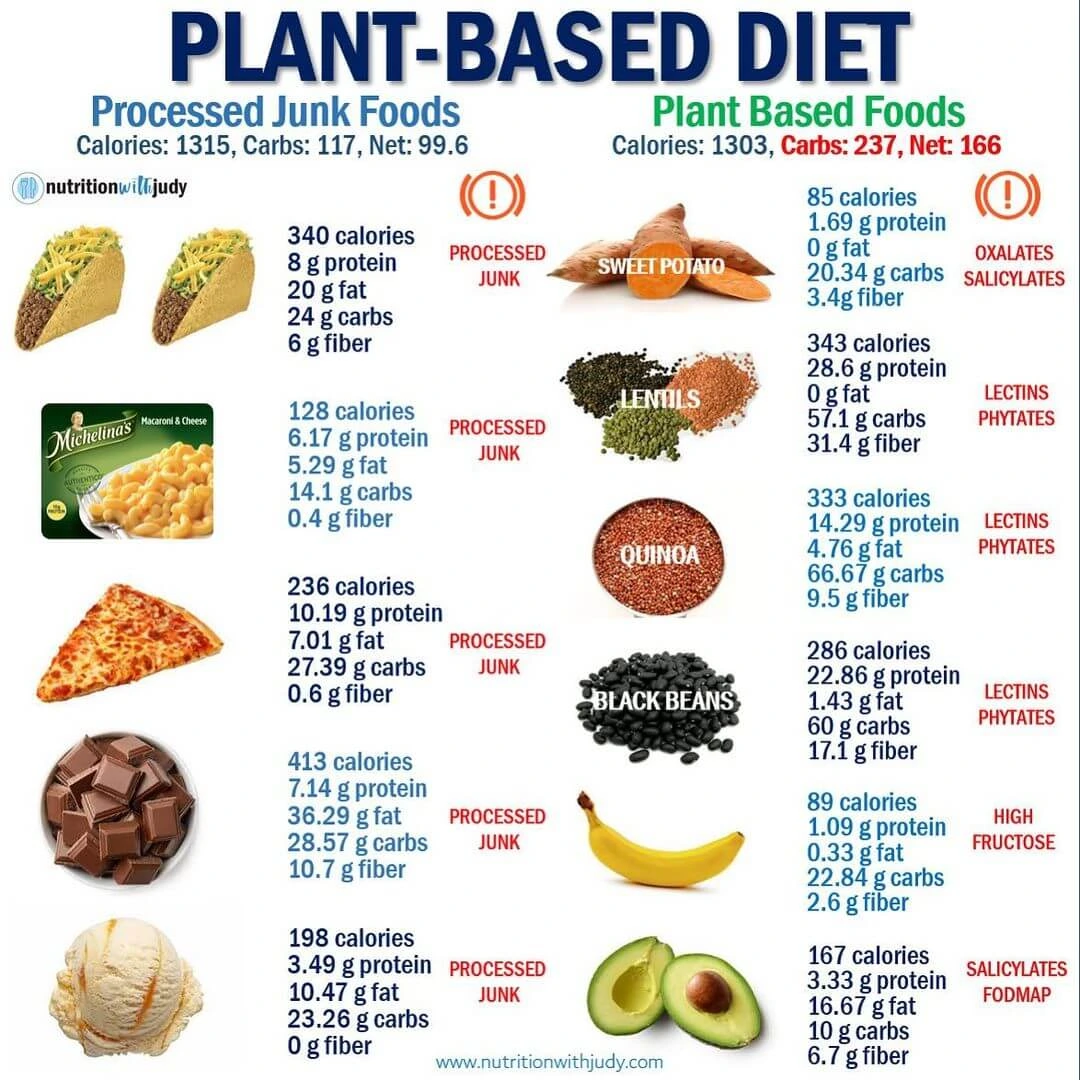
Impact on weight loss
One of the benefits often associated with plant-based diets is weight loss. Plant-based diets tend to be lower in calories and higher in fiber compared to animal-based diets, making them effective for weight management.
The high fiber content in plant-based foods promotes a feeling of fullness, reducing the tendency to overeat. Additionally, plant-based diets are generally lower in saturated fats and higher in complex carbohydrates, which can aid in weight loss.
However, it is important to note that weight loss is not guaranteed solely by following a plant-based diet. It is essential to maintain a balanced and calorie-controlled diet, along with regular physical activity, for successful and sustainable weight loss.
Plant-based diet and disease prevention
The high fiber content and nutrient density of plant-based foods contribute to improved cardiovascular health. A plant-based diet can help lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and improve overall heart health.
Furthermore, research has shown that plant-based diets may help prevent and manage type 2 diabetes. Plant-based foods are typically lower on the glycemic index, meaning they have less impact on blood sugar levels. The high fiber content also aids in blood sugar control.
Some studies have also suggested that plant-based diets may lower the risk of certain types of cancer, such as colorectal, breast, and prostate cancer. The antioxidants and phytochemicals found in plant-based foods have been linked to cancer prevention and cell protection.
The future of plant-based food
As environmental concerns continue to grow, and more individuals recognize the health benefits of plant-based food, it is clear that this dietary choice is here to stay. The increasing popularity of plant-based diets is not only beneficial for personal well-being but also for the planet.
By adopting a plant-based diet, individuals can improve their health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. With the abundance of plant-based options available and the growing awareness of the positive impact of plant-based eating, it is easier than ever to make the transition to a plant-based lifestyle.
Whether it’s for personal health reasons, ethical considerations, or environmental concerns, embracing a plant-based diet can have a profound impact on individuals and the world as a whole. By choosing plants over animal products, we are making a conscious decision to prioritize our health and the health of the planet. The future of plant-based diets looks promising, and the benefits they offer are undeniable. So why not take the first step towards a plant-based lifestyle today? Your body and the environment will thank you.
If you found this article enlightening and are interested in exploring more about current global trends, we invite you to read our article on the Europe Far-Right Trend. This piece delves into the political shifts happening across Europe, providing insights into the rise of far-right ideologies and their implications. Understanding these trends is crucial in comprehending the changing political landscape in Europe and its impact on global affairs.



